Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Mn
Mn清水 一行*; 西村 克彦*; 松田 健二*; 赤丸 悟士*; 布村 紀男*; 並木 孝洋*; 土屋 大樹*; Lee, S.*; 髭本 亘; 都留 智仁; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 245, p.116051_1 - 116051_6, 2024/05
質量ppmレベルの水素は金属材料の水素脆化を引き起こすが、水素の捕獲部位を実験的に解明することは極めて困難である。我々は、正ミュオンが水素の軽い同位体として作用することを利用して、物質中の水素の捕獲状態を研究した。ゼロ磁場ミュオンスピン緩和実験と密度汎関数理論(DFT)計算をAl Mnに対して行った。Al
Mnに対して行った。Al Mnにおける水素のDFT計算の結果、4つの水素トラップサイトが見つかり、その水素トラップエネルギーはeV/atom単位で0.168(サイト1), 0.312(サイト2), 0.364(サイト3), 0.495(サイト4)であった。推定された双極子磁場幅の温度変化(
Mnにおける水素のDFT計算の結果、4つの水素トラップサイトが見つかり、その水素トラップエネルギーはeV/atom単位で0.168(サイト1), 0.312(サイト2), 0.364(サイト3), 0.495(サイト4)であった。推定された双極子磁場幅の温度変化( )は、94, 193, 236Kでステップ状の変化を示した。サイト密度を考慮すると、観測された
)は、94, 193, 236Kでステップ状の変化を示した。サイト密度を考慮すると、観測された の変化温度は、サイト1, 3, 4にミュオンがトラップされたものと解釈される。
の変化温度は、サイト1, 3, 4にミュオンがトラップされたものと解釈される。
Tang, J.*; Wang, Y.*; 藤原 比呂*; 清水 一行*; 平山 恭介*; 海老原 健一; 竹内 晃久*; 上椙 真之*; 戸田 裕之*
Scripta Materialia, 239, p.115804_1 - 115804_5, 2024/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金の外部および内部水素(H)の組合せによって誘起される応力腐食割れ(SCC)の挙動をその場3次元評価技術を使い系統的に調べた。Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金のSCCは水素濃度が臨界値を超える潜在的なクラック発生領域で発生・進展し、Hがナノスケール -MgZn
-MgZn 析出物界面での原子結合を弱め巨視的な割れを引き起こしていることが分かった。さらに、水環境からき裂へ浸透した外部Hが、き裂先端近傍に勾配を持つH影響ゾーンを作ることでSCCにおいて重要な役割を果たすことや、あらかじめ存在する内部Hが、塑性変形に伴いき裂先端に向かうことでSCCにおけるき裂の発生と進展の両方に関与することも分かった。
析出物界面での原子結合を弱め巨視的な割れを引き起こしていることが分かった。さらに、水環境からき裂へ浸透した外部Hが、き裂先端近傍に勾配を持つH影響ゾーンを作ることでSCCにおいて重要な役割を果たすことや、あらかじめ存在する内部Hが、塑性変形に伴いき裂先端に向かうことでSCCにおけるき裂の発生と進展の両方に関与することも分かった。
段野下 宙志*; 長谷川 寛*; 樋口 翔*; 松田 広志*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; 梅澤 修*
Scripta Materialia, 236, p.115648_1 - 115648_5, 2023/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Work-hardening behavior of a lath martensitic Fe-18Ni alloy during tensile deformation is discussed based on the Taylor's equation. The dislocation characteristics are monitored using in situ neutron diffraction. In the specimens of as-quenched (AQ) and tempered at 573 K (T573), the dislocations are extremely dense and randomly arranged. The dislocations in AQ and T573 form dislocation cells as deformation progresses. Consequently, a composite condition comprising cell walls and cell interiors is formed, and the coefficient  in the Taylor's equation increases. Cells are already present in the specimen tempered at 773 K (T773), which has a low dislocation density and a large fraction of edge-type dislocations. As deformation continues, the dislocation density of T773 increases, its cell size decreases, and its composite condition become stronger. Simultaneously, the edge-type dislocation fraction decreases, keeping
in the Taylor's equation increases. Cells are already present in the specimen tempered at 773 K (T773), which has a low dislocation density and a large fraction of edge-type dislocations. As deformation continues, the dislocation density of T773 increases, its cell size decreases, and its composite condition become stronger. Simultaneously, the edge-type dislocation fraction decreases, keeping  unchanged. Thus, both the dislocation arrangement and character affected
unchanged. Thus, both the dislocation arrangement and character affected  , thereby affecting the work-hardening behavior.
, thereby affecting the work-hardening behavior.
 ders band deformation in an ultrafine grain stainless steel by combining
ders band deformation in an ultrafine grain stainless steel by combining  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation analysis
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation analysisMao, W.; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 辻 伸泰*
Scripta Materialia, 235, p.115642_1 - 115642_6, 2023/10
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)本研究では、巨大なリューダースバンド変形を示す超微細粒(UFG)ステンレス鋼の引張その場中性子回折とデジタル画像相関測定を行い、バンド伝播中の歪硬化に対するオーステナイト母相と変形誘起マルテンサイトの個々の寄与を評価した。定量的解析の結果、UFG構造によって流動応力が大幅に増加した場合、オーステナイト母相のひずみ硬化は均一な変形を維持するには不十分であることがわかった。リューダースバンドの伝播に必要なひずみ硬化は、マルテンサイトの形成とその内部の高い内部応力によってもたらされた。
 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction studyGong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Zheng, R.*; 眞山 剛*; Sun, B.*; 相澤 一也; Harjo, S.; 辻 伸泰*
Scripta Materialia, 225, p.115161_1 - 115161_5, 2023/03
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:45.58(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Deformation behavior during uniaxial compression at 21 K and 298 K in a commercial AZ31 magnesium alloy was studied by  neutron diffraction. Decreasing the deformation temperature resulted in a slight increase in yield stress (115 MPa
neutron diffraction. Decreasing the deformation temperature resulted in a slight increase in yield stress (115 MPa  139 MPa), but a remarkable enhancement in both the fracture stress (365 MPa
139 MPa), but a remarkable enhancement in both the fracture stress (365 MPa  551 MPa) and fracture strain (12.8%
551 MPa) and fracture strain (12.8%  16.5%). The low temperature sensitivity of the {10
16.5%). The low temperature sensitivity of the {10 2} extension twinning which governed the macroscopic yielding led to the slight increase in yield stress. At 21K, basal slip was suppressed, while the extension twinning was promoted resulted in higher twin volume fraction. In the late stage of deformation, the {10
2} extension twinning which governed the macroscopic yielding led to the slight increase in yield stress. At 21K, basal slip was suppressed, while the extension twinning was promoted resulted in higher twin volume fraction. In the late stage of deformation, the {10 1}-{10
1}-{10 2} double twinning was suppressed, which is considered to be the reason to delay the fracture at 21 K.
2} double twinning was suppressed, which is considered to be the reason to delay the fracture at 21 K.
土田 紀之*; 上路 林太郎*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.
Scripta Materialia, 222, p.115002_1 - 115002_6, 2023/01
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:64.46(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The present study investigated the tensile deformation behavior of quenched and tempered martensite steels at various austenitization and tempering temperatures using in situ neutron diffraction experiments. Phase lattice strains in the bcc and cementite ( ) phases and dislocation structures in the bcc phase were analyzed. The phase lattice strain in bcc became almost stagnant after yielding as the tempering temperature increased. The phase lattice strain in
) phases and dislocation structures in the bcc phase were analyzed. The phase lattice strain in bcc became almost stagnant after yielding as the tempering temperature increased. The phase lattice strain in  increased linearly with an increase in the flow stress, independent of the austenitization and tempering temperatures. The stress partitioning between bcc and
increased linearly with an increase in the flow stress, independent of the austenitization and tempering temperatures. The stress partitioning between bcc and  was confirmed after the yielding of bcc, which contributed to the work hardening. The phase stresses of bcc and
was confirmed after the yielding of bcc, which contributed to the work hardening. The phase stresses of bcc and  and their stress partitioning improve the mechanical properties of martensite steels, which can be summarized by the systematic changes in phase lattice strain and dislocation properties due to the austenitization and tempering temperatures.
and their stress partitioning improve the mechanical properties of martensite steels, which can be summarized by the systematic changes in phase lattice strain and dislocation properties due to the austenitization and tempering temperatures.
Wei, D.*; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; 加藤 秀実*
Scripta Materialia, 216, p.114738_1 - 114738_6, 2022/07
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:97.37(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Near-equiatomic single-phase twining-induced plasticity (TWIP) high-entropy alloys (HEAs) exhibit a good combination of strength and ductility, but their modest yield strength requires further improvement. Here, we propose a strategy for markedly enhancing their strength while retaining satisfactory ductility, taking advantage of the temperature dependence of the stacking fault energy. The room-temperature strength of a representative TWIP HEA was improved by the cryogenic pre-deformation-induced dislocations, martensite, nanotwins, and stacking faults. The tensile properties were further tuned by subsequent annealing to obtain partially recovered or recrystallized microstructures. The influence of regulated microstructures on the yield strength was clarified by neutron diffraction line profile analysis. This study presents possibilities for fabricating advanced HEAs by tuning the substructures.
Luo, M.-Y.*; Lam, T.-N.*; Wang, P.-T.*; Tsou, N.-T.*; Chang, Y.-J.*; Feng, R.*; 川崎 卓郎; Harjo, S.; Liaw, P. K.*; Yeh, A.-C.*; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 210, p.114459_1 - 114459_7, 2022/03
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:91.45(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The effect of grain size on strain-controlled low-cycle fatigue (LCF) properties in the CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloys (HEAs) was investigated towards the distinct microstructural developments during cyclic loading at a strain amplitude of  1.0%. A much more prominent secondary cyclic hardening (SCH) behavior at the final deformation stage was observed in the fine-grained (FG) than in the coarse-grained (CG) CoCrFeMnNi. In-situ neutron-diffraction and microscopic examination, strongly corroborated by molecular dynamic (MD) simulations, indicated that dislocation activities from planar slip to wavy slip-driven subgrain structures within the grains acted as the primary cyclic-deformation behaviors in the FG CoCrFeMnNi. Differently observed in the cyclic behavior of the CG CoCrFeMnNi was due to a transition from the planar dislocation slip to twinning.
1.0%. A much more prominent secondary cyclic hardening (SCH) behavior at the final deformation stage was observed in the fine-grained (FG) than in the coarse-grained (CG) CoCrFeMnNi. In-situ neutron-diffraction and microscopic examination, strongly corroborated by molecular dynamic (MD) simulations, indicated that dislocation activities from planar slip to wavy slip-driven subgrain structures within the grains acted as the primary cyclic-deformation behaviors in the FG CoCrFeMnNi. Differently observed in the cyclic behavior of the CG CoCrFeMnNi was due to a transition from the planar dislocation slip to twinning.
椎原 良典*; 金澤 良亮*; 松中 大介*; Lobzenko, I.; 都留 智仁; 香山 正憲*; 森 英喜*
Scripta Materialia, 207, p.114268_1 - 114268_4, 2022/01
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:73.14(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)本研究では、最新の人工ニューラルネットワーク(ANN)ポテンシャルに基づく分子力学を使用した 鉄中の46種類の対称傾角粒界の粒界(GB)エネルギーを評価した。粒界エネルギー計算の精度の検証のため、密度汎関数理論(DFT)に基づく第一原理計算、および古典的な経験ポテンシャルである、埋め込み原子法(EAM)、および修正EAM(MEAM)との比較を行った。その結果、EAMとMEAMはDFTの結果(平均約27%)とは大きく異なっていた一方、ANNポテンシャルによる結果はDFTの結果(平均5%)と非常によく一致していることを確認した。GBの一軸引張計算では、EAMとMEAMにおける延性挙動のアーティファクトが改善され、ANNポテンシャルではDFTで観察されたGBの脆性破壊傾向を再現した。これらの結果は、需要の高い鉄におけるANNポテンシャルの有効性を示している。
鉄中の46種類の対称傾角粒界の粒界(GB)エネルギーを評価した。粒界エネルギー計算の精度の検証のため、密度汎関数理論(DFT)に基づく第一原理計算、および古典的な経験ポテンシャルである、埋め込み原子法(EAM)、および修正EAM(MEAM)との比較を行った。その結果、EAMとMEAMはDFTの結果(平均約27%)とは大きく異なっていた一方、ANNポテンシャルによる結果はDFTの結果(平均5%)と非常によく一致していることを確認した。GBの一軸引張計算では、EAMとMEAMにおける延性挙動のアーティファクトが改善され、ANNポテンシャルではDFTで観察されたGBの脆性破壊傾向を再現した。これらの結果は、需要の高い鉄におけるANNポテンシャルの有効性を示している。
Naeem, M.*; He, H.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Zhang, F.*; Wang, B.*; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; Wu, Y.*; Lu, Z.*; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 188, p.21 - 25, 2020/11
被引用回数:56 パーセンタイル:97.51(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The deformation behavior of CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloy was investigated by in situ neutron diffraction at an ultralow temperature of 15 K. Analysis of the diffraction peak widths showed an extremely high dislocation density at 15 K, reaching  10
10 m
m . In addition, the dislocation density was found to closely follow the development of texture caused by deformation. In contrast to deformation by dislocation slip at room temperature, the ultralow-temperature deformation also involved stacking faults, twinning and serrations. The deformation pathway at ultralow temperature is outlined which is responsible for the extraordinary strength-ductility combination.
. In addition, the dislocation density was found to closely follow the development of texture caused by deformation. In contrast to deformation by dislocation slip at room temperature, the ultralow-temperature deformation also involved stacking faults, twinning and serrations. The deformation pathway at ultralow temperature is outlined which is responsible for the extraordinary strength-ductility combination.
山下 享介; 諸岡 聡; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 古賀 紀光*; 梅澤 修*
Scripta Materialia, 177, p.6 - 10, 2020/03
被引用回数:31 パーセンタイル:90.48(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) neutron diffraction measurements during tensile tests at low temperatures of a low alloy steel containing retained austenite have been performed. Evolutions of phase fractions and phase stresses were analyzed and discussed with the progress of deformation. The role of austenite in the steel during deformation at low temperatures was observed not to directly in the contribution to the strengths but in the improvement of the elongation by transformation of austenite to martensite -and in the increasing of the work-hardening rate by an increase in the phase fraction of martensite and the work hardening of martensite.
neutron diffraction measurements during tensile tests at low temperatures of a low alloy steel containing retained austenite have been performed. Evolutions of phase fractions and phase stresses were analyzed and discussed with the progress of deformation. The role of austenite in the steel during deformation at low temperatures was observed not to directly in the contribution to the strengths but in the improvement of the elongation by transformation of austenite to martensite -and in the increasing of the work-hardening rate by an increase in the phase fraction of martensite and the work hardening of martensite.
 113
113 deformation twinning in metastable
deformation twinning in metastable  -type Ti alloy focusing on stress-induced
-type Ti alloy focusing on stress-induced 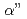 martensite phase
martensite phaseCho, K.*; 森岡 亮太*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 安田 弘行*
Scripta Materialia, 177, p.106 - 111, 2020/03
被引用回数:35 パーセンタイル:92.02(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Deformation behavior of Ti-12Mo alloy which is primarily deformed by {332} 113
113 deformation twinning was studied by in situ neutron diffraction measurements and deformation structure analyses, focusing on the formation of stress-induced
deformation twinning was studied by in situ neutron diffraction measurements and deformation structure analyses, focusing on the formation of stress-induced 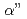 martensite phase. We directly observed for the first time that the
martensite phase. We directly observed for the first time that the 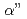 phase was formed at the initial stage of the plastic deformation and the volume fraction of the phase increased with increasing plastic deformation. This stress-induced
phase was formed at the initial stage of the plastic deformation and the volume fraction of the phase increased with increasing plastic deformation. This stress-induced 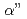 martensite phase acts as a nucleation site for the {332}
martensite phase acts as a nucleation site for the {332} 113
113 twins. Further increase in stress results in a replacement of the
twins. Further increase in stress results in a replacement of the 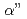 phase by the {332}
phase by the {332} 113
113 twins.
twins.
庄司 衛太*; 磯谷 祥世*; 鈴木 陸人*; 久保 正樹*; 塚田 隆夫*; 甲斐 哲也; 篠原 武尚; 松本 吉弘*; 福山 博之*
Scripta Materialia, 175, p.29 - 32, 2020/01
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:78.21(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The effect of melt convection on the phase separation structures in undercooled Cu- Co alloys was investigated using the electromagnetic levitation technique, where the melt convection was controlled by applying a static magnetic field. The three-dimensional phase separation structures of the solidified Cu-Co alloys were first observed using neutron computed tomography. A large number of small spherical Co-rich phases were dispersed in the Cu-rich phase matrix when the static magnetic field was relatively small. In contrast, several coalesced Co-rich phases, which were elongated along the direction of the static magnetic field, appeared in the higher strength of static magnetic field.
 neutron diffraction analysis during thermomechanical processing
neutron diffraction analysis during thermomechanical processing柴田 曉伸*; 竹田 泰成*; Park, N.*; Zhao, L.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Gong, W.*; 辻 伸泰*
Scripta Materialia, 165, p.44 - 49, 2019/05
被引用回数:29 パーセンタイル:85.46(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Nowadays, a new concept of process utilizing dynamic ferrite transformation, which can achieve ultrafine-grained structure with a mean grain size of approximately 1 m, has been proposed. This paper reports transformation mode of dynamic ferrite transformation and formation mechanism of ultrafine-grained structure revealed by our novel technique of
m, has been proposed. This paper reports transformation mode of dynamic ferrite transformation and formation mechanism of ultrafine-grained structure revealed by our novel technique of  neutron diffraction analysis during thermomechanical processing. Dynamic ferrite transformation occurs in a diffusional manner, whose partitioning behavior changes from para- to ortho-equilibrium with the progress of transformation. Moreover, we propose that dynamic recrystallization of dynamically-transformed ferrite is the main mechanism for the formation of ultrafine-grained structure.
neutron diffraction analysis during thermomechanical processing. Dynamic ferrite transformation occurs in a diffusional manner, whose partitioning behavior changes from para- to ortho-equilibrium with the progress of transformation. Moreover, we propose that dynamic recrystallization of dynamically-transformed ferrite is the main mechanism for the formation of ultrafine-grained structure.
 neutron diffraction study of phase stress evolution in a ferrous medium-entropy alloy under low-temperature tensile loading
neutron diffraction study of phase stress evolution in a ferrous medium-entropy alloy under low-temperature tensile loadingBae, J. W.*; Kim, J. G.*; Park, J. M.*; Woo, W.*; Harjo, S.; Kim, H. S.*
Scripta Materialia, 165, p.60 - 63, 2019/05
被引用回数:24 パーセンタイル:79.52(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Phase stress evolution of face-centered cubic (FCC) and deformation-induced body-centered cubic (BCC) phases was measured in recently developed ferrous medium-entropy alloy. This was done during tensile deformation at -137 C using
C using  neutron diffraction measurement for the quantitative interpretation of the role of martensitic transformation on the improved low-temperature tensile properties. The strain-hardening rate curve exhibits two-stage hardening behavior, and the phase stress and stress contribution from the BCC phase increases significantly while that from FCC phase decreases during plastic deformation. This is a direct demonstration that BCC phase contributes significantly to the increase in strength and strain hardening.
neutron diffraction measurement for the quantitative interpretation of the role of martensitic transformation on the improved low-temperature tensile properties. The strain-hardening rate curve exhibits two-stage hardening behavior, and the phase stress and stress contribution from the BCC phase increases significantly while that from FCC phase decreases during plastic deformation. This is a direct demonstration that BCC phase contributes significantly to the increase in strength and strain hardening.
Wang, B.*; He, H.*; Naeem, M.*; Lan, S.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Nie, Y.*; Wang, X.-L.*; 他7名*
Scripta Materialia, 155, p.54 - 57, 2018/10
被引用回数:57 パーセンタイル:95(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The deformation behavior of an equi-atomic face-centered-cubic CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy was investigated by in-situ neutron diffraction under tensile loading up to 40% applied strain. A three-stage deformation behavior was fully captured by lattice strain and texture evolution. In spite of the chemical complexity, the deformation in CoCrFeNi is dominated by dislocation activities. Analysis of diffraction and microscopy data shows that the deformation progresses from dislocation slip to severe entanglement, where a sharp increase in dislocation density was observed. The neutron diffraction data, corroborated by transmission electron microscopy analysis, provided microscopic insights of the previously reported three-stage hardening behavior.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffraction友田 陽*; Gong, W.*; Harjo, S.; 篠崎 智也*
Scripta Materialia, 133, p.79 - 82, 2017/05
被引用回数:24 パーセンタイル:74.12(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The microstructure evolution during reverse transformation of a Cr-Ni-Mo steel consisting of tempered lath martensite and Cr carbide was examined using  neutron diffraction at high temperatures. The microstructural change from a reversed coarse-grained structure to a fine-grained polygonal structure by further annealing was monitored through a decrease in the diffraction intensity caused by primary extinction and the full width at half maximum. This result is different from that for a bainite steel, showing good coincidence with the observations using electron back scatter diffraction.
neutron diffraction at high temperatures. The microstructural change from a reversed coarse-grained structure to a fine-grained polygonal structure by further annealing was monitored through a decrease in the diffraction intensity caused by primary extinction and the full width at half maximum. This result is different from that for a bainite steel, showing good coincidence with the observations using electron back scatter diffraction.
染川 英俊*; 都留 智仁
Scripta Materialia, 130, p.114 - 118, 2017/03
被引用回数:25 パーセンタイル:74.12(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)マグネシウムのき裂進展挙動に対する合金元素の影響と{10 2}型の双晶境界における原子レベルの挙動について、実験と計算によって検討した。その結果、実験から合金元素が明確にき裂進展挙動に影響することがわかった。計算によって、閉殻な軌道を銀や亜鉛などの合金ではマグネシウムの双晶境界を強化する傾向があることがわかった。
2}型の双晶境界における原子レベルの挙動について、実験と計算によって検討した。その結果、実験から合金元素が明確にき裂進展挙動に影響することがわかった。計算によって、閉殻な軌道を銀や亜鉛などの合金ではマグネシウムの双晶境界を強化する傾向があることがわかった。
 -phase and high-pressure
-phase and high-pressure  -phase of pure group IV transition metals
-phase of pure group IV transition metals足立 望*; 戸高 義一*; 鈴木 裕士; 梅本 実*
Scripta Materialia, 98, p.1 - 4, 2015/03
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:56.3(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)中性子回折法により第IV族遷移純金属の高圧 相の変形集合組織を評価した。
相の変形集合組織を評価した。 0001
0001
 方位は高圧ねじり過程により導入されたせん断ひずみの増加によりせん断方向に徐々に揃う様子が確認された。変形集合組織は、
方位は高圧ねじり過程により導入されたせん断ひずみの増加によりせん断方向に徐々に揃う様子が確認された。変形集合組織は、 相の主すべり系が{11-20}
相の主すべり系が{11-20} 0001
0001
 であることを示唆している。逆変態
であることを示唆している。逆変態 相に対する機械的に安定した
相に対する機械的に安定した 相の方位関係を観察した結果、SilcockおよびRabinkinにより提案された方位関係と似ていることを確認した。
相の方位関係を観察した結果、SilcockおよびRabinkinにより提案された方位関係と似ていることを確認した。
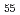 Al
Al Ni
Ni Cu
Cu bulk metallic glass containing ZrC particles by synchrotron X-ray diffraction
bulk metallic glass containing ZrC particles by synchrotron X-ray diffraction鈴木 裕士; 才田 淳治*; 菖蒲 敬久; 勝山 仁哉; 加藤 秀実*; 今福 宗行*; 佐藤 成男*
Scripta Materialia, 66(10), p.801 - 804, 2012/05
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:37.98(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)10vol.%ZrC粒子分散Zr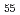 Al
Al Ni
Ni Cu
Cu 四元系金属ガラスについて、圧縮変形させた試験片内部のZrC相及び金属ガラス相の残留ひずみを放射光X線により測定するとともに、有限要素解析によりZrC粒子周辺の局所的な塑性変形挙動を評価することによって、その圧縮変形メカニズムを評価した。その結果、変形初期においては、粒子周囲に局所的な塑性変形を生じるとともに、金属ガラス相が大きくひずみを負担するが、変形が進むと金属ガラス相が全体的に降伏して粒子が大きくひずみを負担、最終的には粒子が粒内破壊を生じて破断に至ることを明らかとした。
四元系金属ガラスについて、圧縮変形させた試験片内部のZrC相及び金属ガラス相の残留ひずみを放射光X線により測定するとともに、有限要素解析によりZrC粒子周辺の局所的な塑性変形挙動を評価することによって、その圧縮変形メカニズムを評価した。その結果、変形初期においては、粒子周囲に局所的な塑性変形を生じるとともに、金属ガラス相が大きくひずみを負担するが、変形が進むと金属ガラス相が全体的に降伏して粒子が大きくひずみを負担、最終的には粒子が粒内破壊を生じて破断に至ることを明らかとした。